The Essence of an Entrepreneur.
The success of any firm depends largely on how an entrepreneur is able to find a balance between his opportunities and available resources. He must be creative, self-motivated and also have a strong urge to succeed
What is “Entrepreneurship”?
Entrepreneurship is the process of creating something new with value by devoting the necessary time and effort, assuming the accompanying financial, psychic and social rewards of monetary and personal satisfaction and independence.
This definition stresses four basic aspects of being an entrepreneur regardless of the field. First, entrepreneurship involves the creation process creating something new of value. Secondly, entrepreneurship requires the devotion of necessary time and effort. Assuming the necessary risks is the third aspect of entrepreneurship. These risks take a variety of forms, depending on the field of effort of the entrepreneur, but usually centre around financial, psychic and social areas. The final part of the definition involves the rewards of being an entrepreneur. The most important of these rewards is independence, followed by personal satisfaction.
In almost all the definitions of entrepreneurship, there is agreement that we are talking about a kind of behaviour.
WHAT IT INVOLVES
- Initiative taking.
- The organising and reorganising of social and economic mechanisms to turn resources and Situations to practical account
- The acceptance of risk or take risks and failure
Many of these traits are lightly inter-related. That is people who are to confident will probably accept responsibility for their own decisions, and will be willing to take risks and become leaders. Not all entrepreneurs are alike, either in the above mentioned traits or in their personal qualities. Some are aloof and arrogant; some are warm and friendly; some are withdrawn and shy. But, when measured on various personal traits and skills, it is clear that, as a group, entrepreneurs differ from non -entrepreneurs.
Entrepreneurship results in the creation, enhancement, realisation and renewal of value, not just for the owners, but for all participants and stakeholders. It requires a willingness to take risks -both personal and financial – but, in a very calculated fashion in order to constantly shift the odds to your favour, balancing the risks with the potential rewards. Entrepreneurial leaders inject imagination, motivation, commitment, passion, tenacity, integrity, teamwork and vision. They face dilemmas and must make decisions despite ambiguity and contradictions. Very rarely is entrepreneurship a get-rich quick proposition; rather it’s one of building -and continually renewing- long term value and durable cash flow.
Entrepreneurs with right characteristics don’t think much about taking risks or getting rich. Instead they are
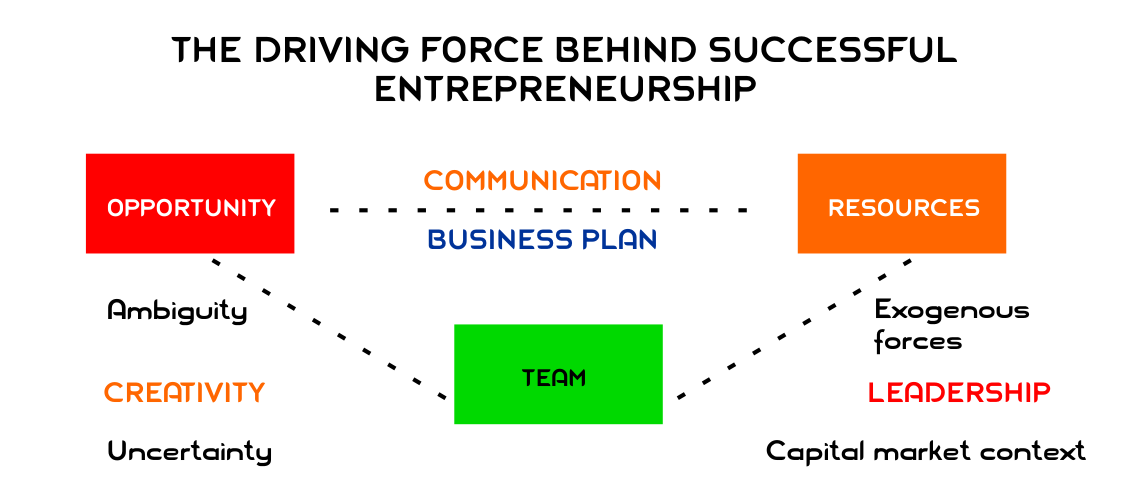
THE DRIVING FORCE BEHIND SUCCESSFUL ENTREPRENEURSHIP
The above model as explained, starts with opportunity, not money, nor strategy, nor a network, nor a team and nor the business plan. Genuine opportunities are much bigger than either the talent or the capacity of the team or the resources available to the team. .The role of the entrepreneur and the team is to juggle all these key elements in a dynamic, moving environment- find the right opportunity, which can be exploited effectively with the resources available, along with the team.
Obsessed with building a mousetrap. One reason entrepreneurs – the ones most likely to make it, at least behave like men and women possessed, is that they have experienced a flash of understanding known as ”entrepreneurial insight“. They have seen in their mind’s eye, the better mousetrap, the greater unmet need, the changing tide, the big opportunity. Because they see it so clearly, they feel that they know exactly what must be done to prevail.
For some, entrepreneurial insight isn’t a one-time flash but instead a unique way of viewing and valuing opportunities. Successful entrepreneurs have that insight and the enthusiasm that comes with it which gets them far. Over confidence can be a problem though. It is called arrogance and it often trips up aspiring entrepreneurs. A good entrepreneur should not be driven by arrogance nor must be affected by its close relative: a big ego. The arrogant person is devoted to himself. He/she thinks, that he/she has all the answers, accepts no advice and blames others for his/her failure.
Nearly all entrepreneurs are comfortable with -if not eager for – risky, unfamiliar situations.
Every authority on entrepreneurship recognises the importance of self-motivation for entrepreneurial success. .Self -motivated people do not blame external forces for events to their lives. They believe that their own efforts and abilities can shape their destiny. This quality of character –“internal locus of control” – is a bottom line characteristic of successful entrepreneurs.
Five most frequent factors that have been related to entrepreneurial performances are
- AUTONOMY : Independent actions and self direction
- INNOVATIVENESS : New ideas, experimentation and creativity
- RISK TAKING : Venturing into uncertainty and committing assets
- PROACTIVENESS : Acting in anticipation of future problems or needs
- COMPETITIVE AGGRESSIVENESS : Strongly challenging competition to achieve entry or improve position
A contingency model of entrepreneurial venturing is of value to the inexperienced and unsophisticated new business persons as well as to the established entrepreneurs. Of the five variables cited above, innovation and risk are the easiest for an entrepreneur to grasp and measure. Compared to autonomy, proactiveness, and competitive aggressiveness, these two variables can be more concretely defined and can better fit the specific examples of an entrepreneurial venture.
Innovation is defined as the Creation of something new and different. In terms of measurement, the newer and more different the proposed product or services, the higher it would be scored on a measurement scale. Risk is defined as the probability of major financial loss. Measuring risk involves not only estimating the probabilities of various levels of success and failure outcomes, along with the quantitative levels of those outcomes, but also the impact of possible negative outcomes on the entrepreneur’s specific financial conditions.
Within a company or an industry, opportunities for innovation can be found in unexpected occurrences, incongruities of various kinds, process needs, or changes in an industry or market. Outside a company, opportunities arise from demographic changes, changes in perception, or new knowledge. These seven sources overlap, and the potential for innovation may lie in more than one area at a time.
Innovation like any other endeavour takes talent, ingenuity and knowledge. But if diligence, persistence, and commitment are lacking, companies are unlikely to succeed at the business of innovation. Innovation begins with a conscious search for opportunities. Those opportunities can be categorised but not predicted. Finding those opportunities and exploiting them with focussed, practical solutions requires disciplined work.
Innovation is the specific function of entrepreneurship, whether in an existing business, a public service institution or a new venture sorted by a lone individual in a family kitchen. It is the means by which the entrepreneur either creates new wealth, producing resources, or endows existing resources with enhanced potential for creating wealth.
ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS
The general prerequisites for entrepreneurial activities offered by the region
- The effects of the region on the characteristics on the firms in it.
- The effects of the region on the entrepreneurs heading those firms
In starting a new firm, the role of the entrepreneur is vital because the whole process is often heavily dependent on the work of the entrepreneur and his/her family. The success of the firm can be explained in terms of the characteristics of the firm, the know-how of the entrepreneur, and his/her personality.
“Innovation like any other endeavour takes talent, ingenuity and knowledge. Innovation begins with a conscious search for opportunities”.
WHAT CAN HELP NEW FIRMS
- Most of the firms in the region are small
- Most of the personnel / workers have business managerial know-how
- The level of education in the region is high especially the percentage of persons with high technical education
- Economic life can be characterised as active
- People living in the region have property that can be used as security for a loan
- Industry in the region is not restricted to lines of business where entering the market is difficult
The environmental factors affecting entrepreneurial activities can be grouped into the following categories:Broadly speaking, two different starting points exist for the development of new entrepreneurial activity. On
Broadly speaking, two different starting points exist for the development of new entrepreneurial activity. On the one hand, there are entrepreneurial activities where the main factor is the entrepreneur himself/herself. The entrepreneurial activities are developed as a life strategy on the part of the entrepreneur as a way of making a living and thus very much centred around the entrepreneur’s personality. On the other hand, there are firms already in existence where new ideas for the entrepreneurial activities arise; either side-by-side with the old activities or as an integral part of them.
Even though the risk is a bit higher with high investments, technology allows entrepreneurs to perform their tasks intelligently. Using automation can help reduce the burden of administrative functions and allows entrepreneurs to focus on what they have to do in their business.
To end this, we can say that with bright innovation from entrepreneurs, entrepreneurship has become important and vital to the economic growth. It will help build the country towards a market-oriented economy.
Source: JW